Introduction
Understanding juvenile laws in North Carolina is essential for caregivers navigating the youth justice system. With youth delinquency complaints on the rise and significant legal changes like the 'Raise the Age' law coming into play, caregivers need to be well-informed to advocate effectively for the minors in their care.
Have you ever felt overwhelmed by the complexities of the legal system? It’s crucial to know that you’re not alone in this fight. Caregivers can play a vital role in the rehabilitation process, fostering positive outcomes for young individuals facing legal challenges. How can you ensure that you’re not just informed but actively engaged in this journey?
We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Explore the Basics of North Carolina Juvenile Laws
The focus of North Carolina juvenile laws is to meet the unique needs of minors accused of offenses. Here are some key points to consider:
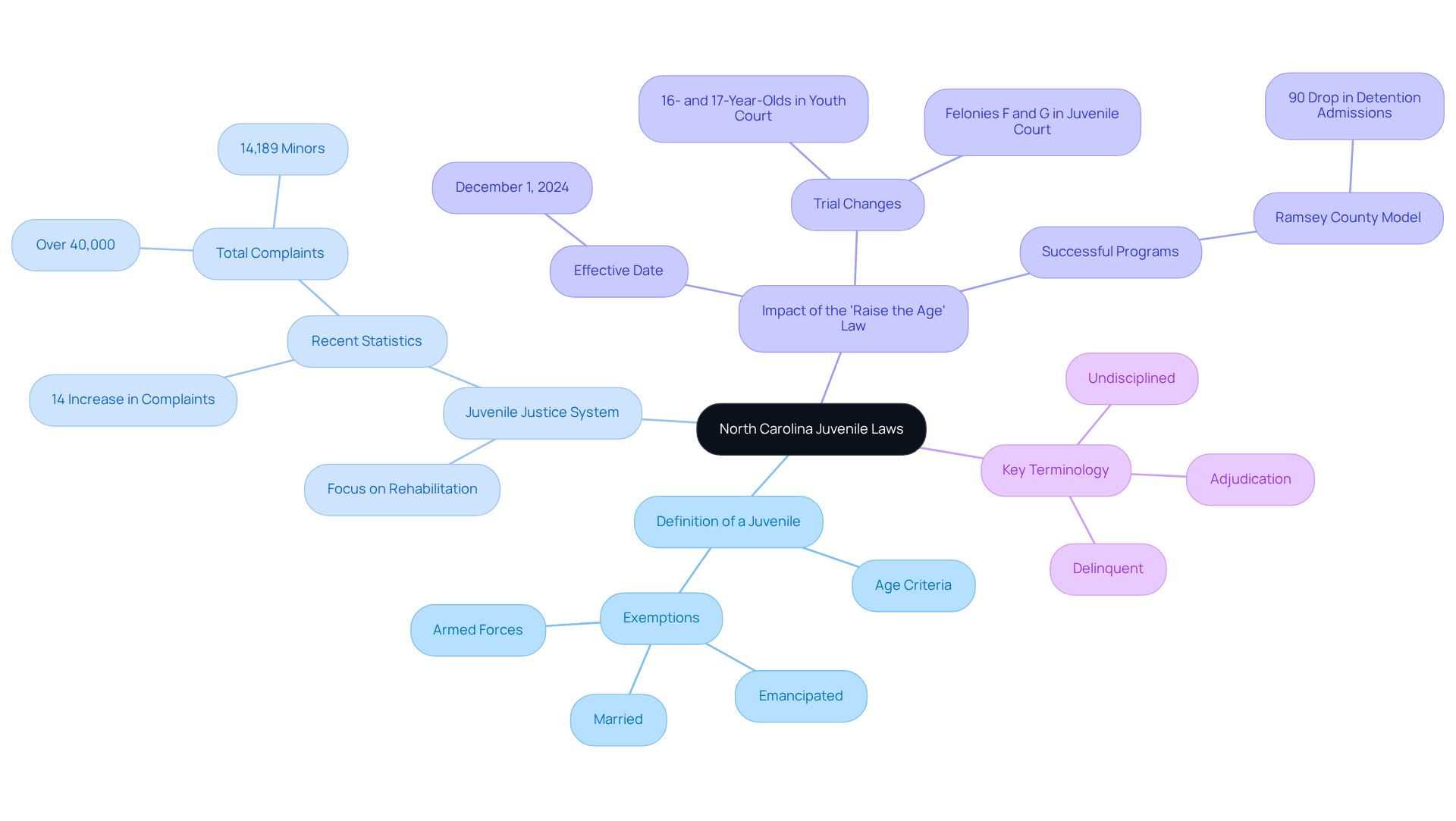
- Definition of a Juvenile: In North Carolina, a juvenile is anyone under 18 who isn’t married, emancipated, or serving in the armed forces.
- Juvenile Justice System: This system emphasizes rehabilitation over punishment, aiming to support and guide young offenders. Recent statistics reveal a concerning trend: from 2022 to 2024, youth delinquency complaints rose by 14%, totaling over 40,000 against 14,189 minors. This increase highlights the urgent need for effective interventions to address the root causes of youth offenses.
- Impact of the 'Raise the Age' Law: Starting December 1, 2024, the 'Raise the Age' law will require that 16- and 17-year-olds charged with certain felonies be tried in youth court instead of adult court. This shift reflects a growing recognition of the importance of rehabilitation as outlined in North Carolina juvenile laws. Successful programs in places like Ramsey County, Minnesota, which saw over a 90% drop in youth detention admissions after implementing structured risk assessment tools, serve as a model for North Carolina's evolving approach to youth justice.
- Key Terminology: It’s crucial to understand terms like 'delinquent,' 'undisciplined,' and 'adjudication' to navigate the youth court process effectively. Knowing these terms helps caregivers advocate for the rights and needs of the young individuals they support.
These foundational aspects equip caregivers with the essential knowledge to navigate the complexities of the youth justice system and advocate for the best outcomes for the young people in their care.
Understand Caregiver Rights and Responsibilities
Caregivers are vital in the youth justice system, and knowing their rights and responsibilities is key to effective advocacy. Here’s what you need to know:
-
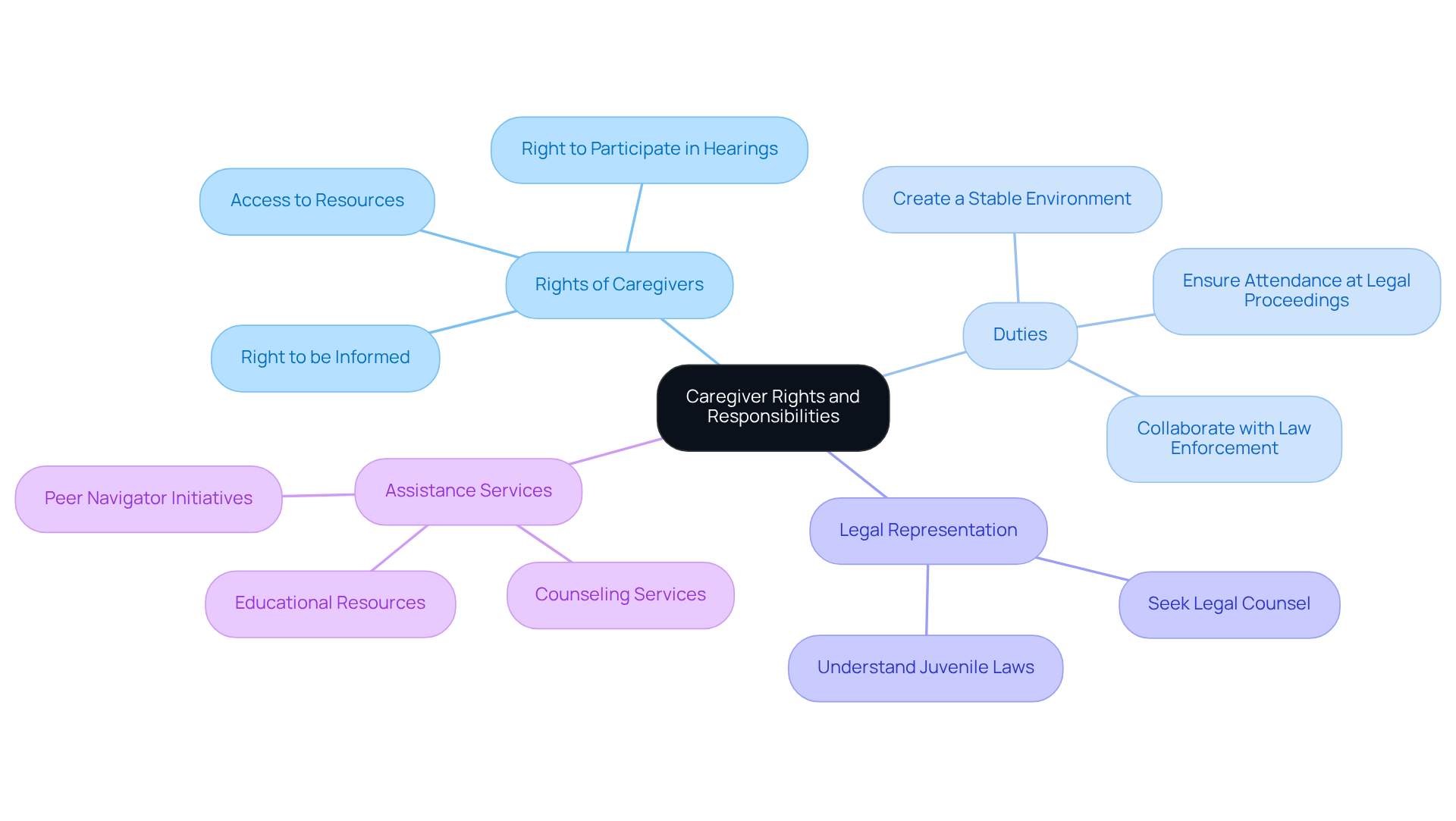
Rights of Caregivers: Caregivers have the right to be informed about the juvenile's legal proceedings, participate in hearings, and access necessary resources for support. Their presence in legal settings can significantly boost the chances of positive outcomes for youth.
-
Duties: Caregivers must create a stable environment, ensure the young person attends legal proceedings, and work alongside law enforcement. It’s common for them to feel emotional stress and blame during court proceedings, which can hinder their engagement. Open communication with youth justice personnel is essential to overcoming these challenges.
-
Legal Representation: Caregivers can seek legal counsel to navigate complex situations, especially if the young person faces serious charges. Understanding North Carolina juvenile laws empowers guardians to advocate effectively for their child's needs.
-
Assistance Services: Familiarize yourself with available assistance services, like counseling and educational resources, that can aid in the young person's rehabilitation. Programs designed to enhance support provider involvement, such as peer navigator initiatives, have shown promise in offering emotional and practical assistance, helping individuals feel more engaged and valued.
By understanding these rights and duties, caregivers can better support the youths in their care and ensure their needs are met within the framework of North Carolina juvenile laws. The importance of caregiver participation cannot be overstated; it directly influences decision-making by law enforcement and court officials at various stages of the youth justice process.
Navigate Resources and Support for Juvenile Offenders
Caregivers face real challenges when supporting young individuals in the justice system. But there’s hope. Here are essential resources that can make a difference:
-
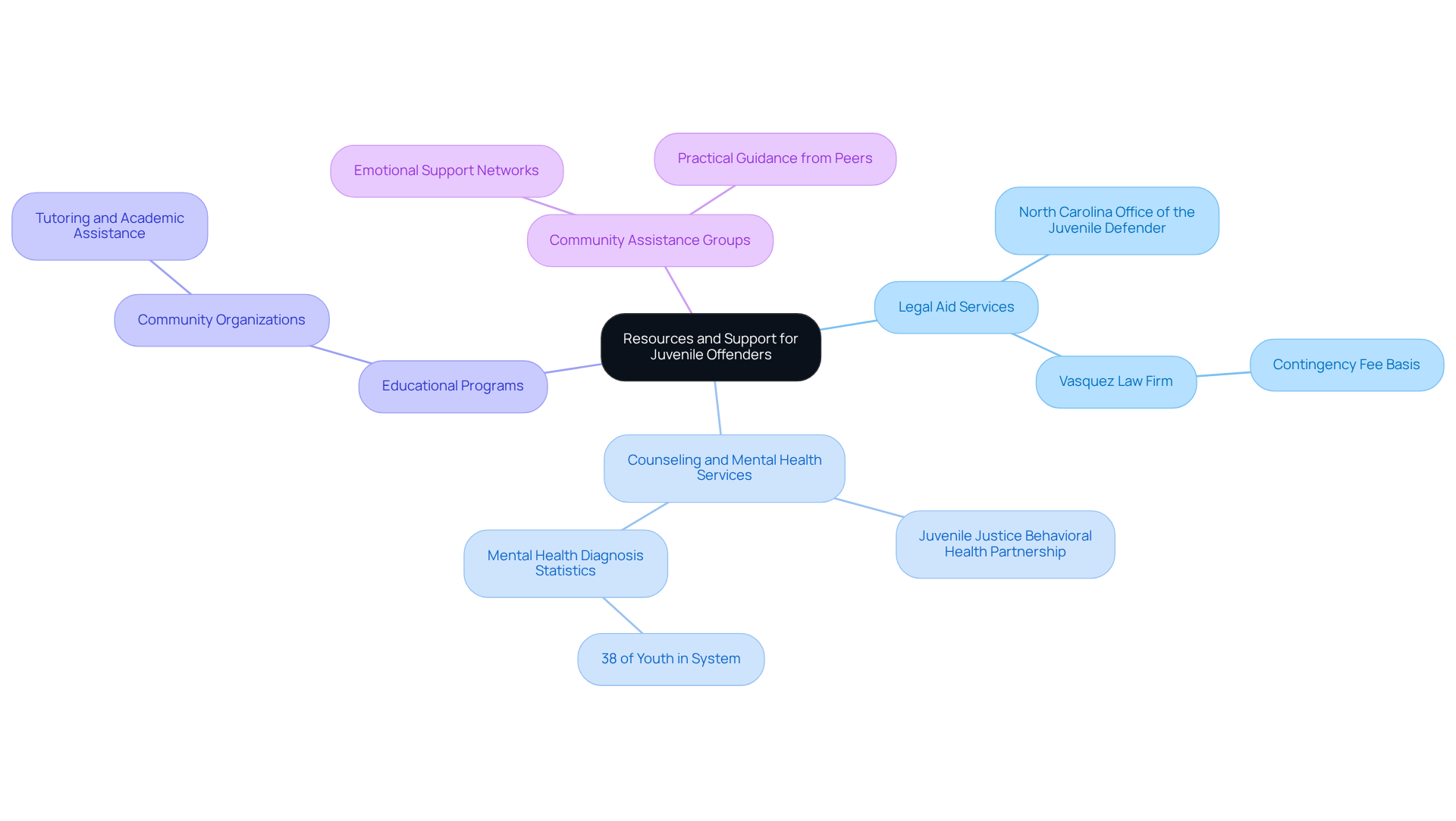
Legal Aid Services: Organizations like the North Carolina Office of the Juvenile Defender provide crucial legal assistance and guidance for juveniles and their caregivers. They ensure that young individuals receive fair representation. The Vasquez Law Firm exemplifies this commitment by working on a contingency fee basis for personal injury cases - families pay nothing unless they win. This approach removes financial barriers to justice.
-
Counseling and Mental Health Services: Access to mental health resources is vital for young individuals facing emotional challenges. Programs like the Juvenile Justice Behavioral Health partnership offer tailored support, addressing the unique needs of youth. With 38% of young individuals in the system having a mental health diagnosis, these services are more important than ever.
-
Educational Programs: Many community organizations provide educational assistance and tutoring for youth, helping them maintain academic progress while navigating legal matters. This support is crucial, especially given the rising youth delinquency complaints in recent years.
-
Community Assistance Groups: Joining assistance groups can provide caregivers with emotional encouragement and practical guidance from others in similar situations. This fosters a sense of community and shared experience.
By utilizing these resources, caregivers can significantly enhance their ability to support juveniles effectively. Remember, you’re not alone in this fight. Together, we can ensure that young individuals receive the guidance and assistance they need during these challenging times.
Conclusion
Understanding North Carolina juvenile laws is crucial for caregivers navigating the youth justice system. With a focus on rehabilitation rather than punishment, and the upcoming changes from the 'Raise the Age' law, there’s a clear shift towards more supportive approaches for minors. By grasping these legal frameworks, caregivers can effectively advocate for the needs and rights of the youth in their care.
Key insights from this guide:
- Define what a juvenile is
- Outline the structure of the juvenile justice system
- Highlight the importance of caregiver involvement
Caregivers need to be aware of their rights and responsibilities, engage in the legal process, and utilize resources like legal aid services and mental health support. These elements are vital for ensuring that young individuals receive the guidance they need to navigate their challenges successfully.
The journey through the juvenile justice system can feel overwhelming. But with the right knowledge and support, caregivers can make a significant difference. It’s essential to stay proactive, seek out resources, and foster open communication with legal personnel. By doing this, caregivers not only advocate for the youth's best interests but also contribute to a more compassionate and effective juvenile justice system in North Carolina. Remember, you’re not alone in this fight-together, we can make a difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the definition of a juvenile in North Carolina?
In North Carolina, a juvenile is defined as anyone under 18 who is not married, emancipated, or serving in the armed forces.
What is the primary focus of the North Carolina juvenile justice system?
The primary focus of the North Carolina juvenile justice system is to emphasize rehabilitation over punishment, aiming to support and guide young offenders.
What recent trend has been observed in youth delinquency complaints in North Carolina?
From 2022 to 2024, youth delinquency complaints in North Carolina rose by 14%, totaling over 40,000 complaints against 14,189 minors, highlighting the urgent need for effective interventions.
What is the 'Raise the Age' law, and when does it take effect?
The 'Raise the Age' law, which takes effect on December 1, 2024, requires that 16- and 17-year-olds charged with certain felonies be tried in youth court instead of adult court.
How does the 'Raise the Age' law reflect changes in juvenile justice?
The 'Raise the Age' law reflects a growing recognition of the importance of rehabilitation in juvenile justice, aligning with North Carolina's evolving approach to youth offenses.
What successful model is mentioned for juvenile justice reform, and what was its impact?
A successful model mentioned is from Ramsey County, Minnesota, which saw over a 90% drop in youth detention admissions after implementing structured risk assessment tools.
Why is it important to understand key terminology in the juvenile justice system?
Understanding key terminology such as 'delinquent,' 'undisciplined,' and 'adjudication' is crucial for navigating the youth court process effectively and advocating for the rights and needs of young individuals.




